Inside the cannabis plant, an intricate system of chemical compounds works together to create the thousands of unique effects experienced when consuming the different strains available on the market. Chief among those compounds are cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids, and other plant material. While terpenes are like the essential oils that control smell and flavor, cannabinoids (and two in particular) drive the mental and physical effects of cannabis consumption. Those two cannabinoids, THC and CBD, we will explore further in this article.
What is THC?
A dominant compound affecting your brain and body is the potent molecule called tetrahydrocannabinol, known as THC to most people. THC has gained notoriety as the cannabinoid that gets you high, but this psychoactive molecule possesses many additional effects that deserve further study. While we only found the compound about 60 years ago, humans have used cannabis as medicine for millennia, with the first recorded use dating back to China in 2727 B.C. in a book written by Emperor Shen Nung, the father of Chinese medicine.
Raphael Mechoulam first discovered THC at Hebrew University in Jerusalem, and the story is remarkable. According to Mechoulam, as quoted in BioMedCentral, “It all started from a fateful bus ride in 1964, when I brought five kilos of Lebanese hashish I received from the Israeli Police to my laboratory at the Weitzman Institute in Rehovot.”
What is CBD?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is another prevalent cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. The significant difference between CBD and THC comes down to the psychoactive effect.
Both compounds work by communicating with receptors. However, unlike THC, CBD does not bind to the CB receptors making CBD non-psychoactive. Since CBD does not bind directly to ECS receptors, it does not stimulate them as THC does to create the well-known “high” feeling. By influencing your ECS receptors indirectly, CBD restores homeostasis (or balance) in the body without psychoactive effect. What makes CBD special is that it has the ability to interact with several receptors in the brain. For example, CBD also communicates with serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A receptor, which may explain why it can help with temporary stress.
How Many Americans Smoke Marijuana?
The most basic statistics you can find about marijuana relate to how many people smoke it or use it, and while there is data going back much further than this, the past decade of data offers a comprehensive look at how many people are using cannabis both within the past year and within the past month.
There has been a consistent increase in the use of cannabis both in the past month and in the past year from 2012 to 2021.
In 2012, 11.6% of US adults had used cannabis in the past year, while 7.1% had done so in the previous month.
By 2021, this had increased to 16.9% of US adults using cannabis in the past year and 11.7% in the previous month, increasing by around 46% and 65% respectively.
This likely reflects the increasing acceptance of cannabis in society, with more and more people both having legal access and being less likely to harbor negative viewpoints about the plant.
What Are the Most Common Reasons for Using Cannabis?
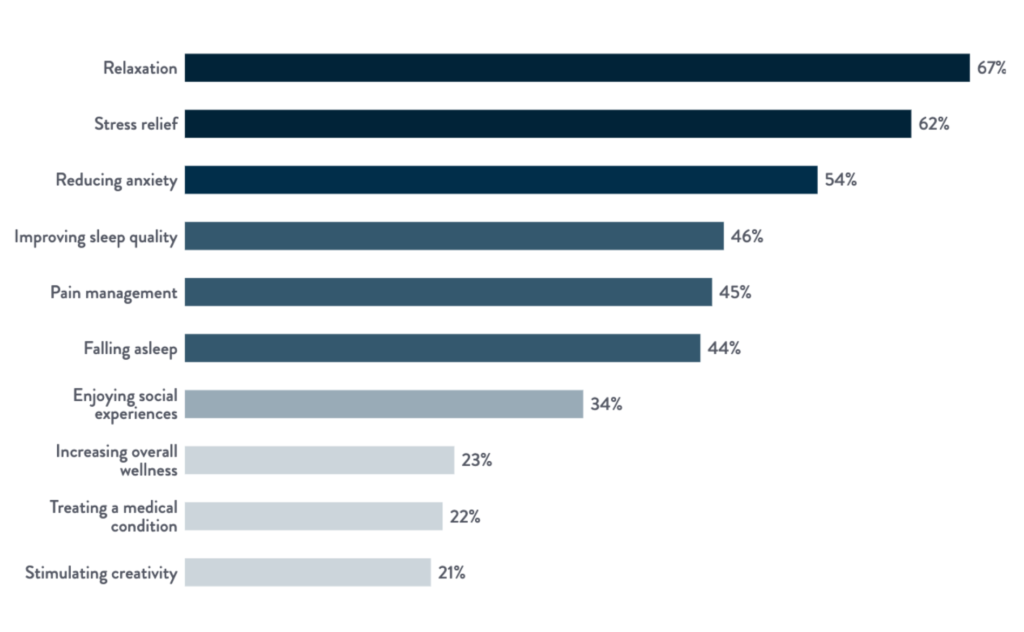
With increasing numbers of people using cannabis, it’s natural to wonder what people give as their motivation for doing so. The top three reasons, given by over half of all respondents, are relaxation (67%), stress relief (62%) and to ease anxiety (54%), with smaller numbers reporting using weed to help with sleep quality (46%), pain (45%) and falling asleep (44%). Less common reasons include smoking for social reasons (34%), overall wellness (23%), for a medical condition (22%) and to enhance creativity (21%).
Post time: Jun-03-2019

